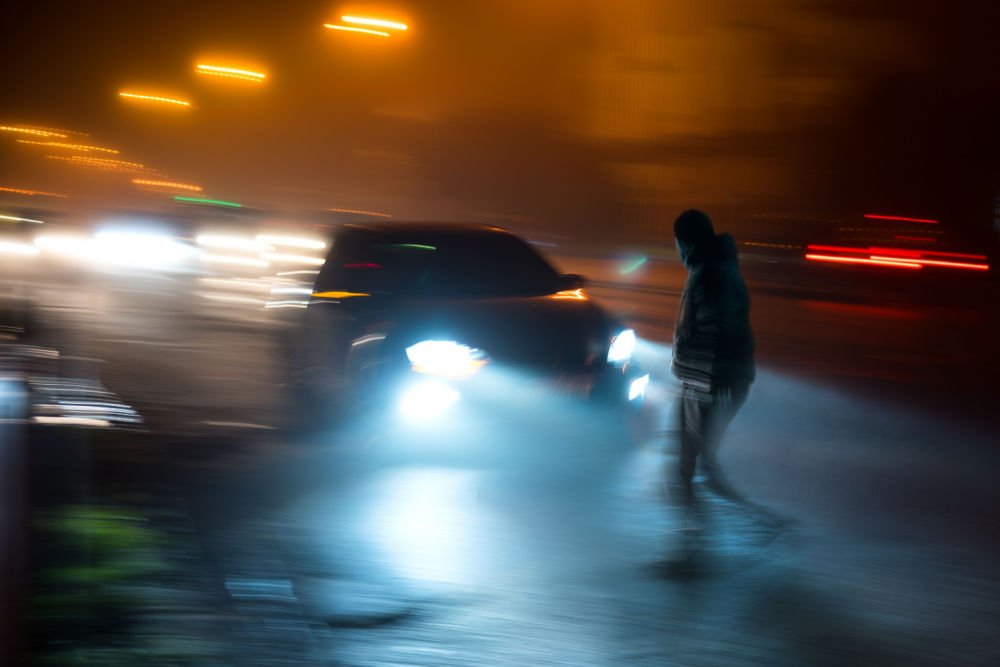

Understanding Pedestrian Accidents
Before diving into the numbers, let's first understand the context of pedestrian age and factors that contribute to pedestrian age related accidents.
Causes of Pedestrian Accidents
There are several factors that can cause a severe injury or serious injury, in pedestrian accidents, most dangerous people including driver inattention, dangerous speeding, failure to yield, and impaired driving. Additionally, pedestrian factors such as inattention, intoxication, and failure to use crosswalks can also contribute to serious, severe injury, or fatal such accidents.
Risk Factors for Pedestrian Accidents
Pedestrian accidents are more likely to be fatal and occur in other vehicles under certain conditions, such as during nighttime, in urban areas, and near intersection and non-intersection locations.
The Impact of Speed on Pedestrian Survival RatesNow that we have a better understanding of pedestrian accidents, let's discuss how the 35 mph speed limit affects higher risk of the pedestrian crashes severe injuries, deaths and survival rates.
Speed and Injury SeverityAs a driver of vehicle that hit someone's speed increases, so does same speed and the force of impact in a collision. This increased force can lead to more severe injuries for the driver of vehicles and pedestrians hit in collisions and the pedestrians hit, reducing their chances of survival.
Speed and Stopping Distance
A higher speed also affects a driver's ability to react and stop their vehicle or driver in time to avoid a collision or crash. The faster a vehicle or driver is traveling, for example at high speeds, for example, the longer it will take the car or driver to stop, increasing the likelihood of an accident or crash.
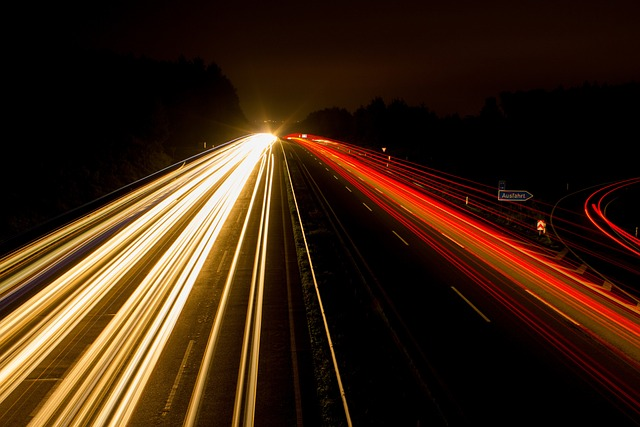

Pedestrian Survival Rate at 40 mph
According to research, the survival fatality rate for pedestrians struck by a vehicle traveling at 40 mph is around 15% - a stark difference when compared to the 90% survival rate for pedestrians killed larger vehicles, at around 20 mph up to 30 mph. 20 mph up to 30 mph. This highlights the importance of speed management in urban areas to ensure pedestrian safety.
Strategies for Reducing Pedestrian Fatalities
There are also many studies and several approaches that can be implemented to reduce serious pedestrian crashes, fatalities, and severe injury, including traffic calming measures, pedestrian infrastructure improvements, public awareness campaigns, and law enforcement and legislation.
Traffic Calming MeasuresTraffic calming measures are physical and visual changes to streets and lanes that encourage drivers to slow down. Examples include speed humps stop signs, through lanes, roundabouts, side lanes and curb extensions.
Pedestrian Infrastructure Improvements Improving pedestrian infrastructure can help reduce the risk of accidents. This can include installing crosswalks, pedestrian signals, and sidewalks, as well as improving street lighting. Public Awareness Campaigns
Public Awareness Campaigns Public awareness campaigns can help educate drivers and pedestrians about the importance of road safety and the consequences of speeding.
Law Enforcement and LegislationStrict enforcement of traffic laws in school zones and the implementation of speed limits in urban areas and school zones can help reduce speeding and improve driver and pedestrian safety.

Conclusion
The survival rate of pedestrians involved in accidents with vehicles traveling at 40 mph or lower speeds is alarmingly low. It is crucial to adoptvarious strategies, such as traffic calming measures, infrastructure improvements, public awareness campaigns, and law enforcement, to reduce higher risk of pedestrian injury and crash fatalities larger vehicles are at lower speeds. Ultimately, creating safer streets for pedestrians and drivers alike depends on a combined effort from all stakeholders, including local governments, transportation agencies, motorists, and the public.

FAQs
1. What is the survival and death rate for pedestrians struck by a vehicle traveling at 40 mph what percent of pedestrians survive the average speeds of 40 mph?The survival rate for pedestrians struck by a vehicle traveling at 40 mph is around 15%. This is significantly lower compared to the 90% survival fatality rate for pedestrians killed those at 40 mph what percent of pedestrians survive being hit when the same speed of a vehicle is hit while traveling at 20 mph to 30 mph only if severely injured.
2. What are some examples of traffic calming measures?Examples of traffic calming measures include, speed limits, humps stop signs, roundabouts, curb extensions, and chicanes. These measures and stop signs to other traffic signals encourage drivers to slow down, improving safety for pedestrians and other road users.
 3. How can pedestrian infrastructure be improved?
3. How can pedestrian infrastructure be improved? Pedestrian infrastructure can be improved by installing or upgrading crosswalks, pedestrian and traffic signals,, and sidewalks, as well as improving street lighting to enhance visibility for drivers of vehicles and pedestrians crossing together.
4. What is the role of public awareness campaigns in reducing pedestrian fatalities?Public awareness campaigns can educate drivers and pedestrians about the importance of road safety, the consequences of speeding, and the need to adhere to traffic rules. These campaigns can help change behaviors and reduce the number of pedestrian deaths and car accidents together.
5. How can law enforcement and legislation contribute to pedestrian safety? Strict enforcement of traffic laws and the implementation of appropriate speed limits, particularly in urban areas with high pedestrian traffic, can help reduce speeding and vehicle speeds and improve driving faster pedestrian safety. Additionally, new legislation aimed at down in vehicle speeds, pedestrian deaths and enhancing road safety can support the development of safer streets and walk through. 6. How does pedestrian behavior contribute to car accidents?Pedestrian behavior can also play a role in accidents. Factors such as inattention, intoxication, and failure to use designated crosswalks can increase the risk of accidents. Encouraging responsible pedestrian behavior, such as using crosswalks, waiting for signals, and being aware of their surroundings, can help reduce the number of accidents.
 7. What is the role of urban planning in pedestrian safety?
7. What is the role of urban planning in pedestrian safety? Urban planning can greatly impact pedestrian safety. By prioritizing walkability, creating pedestrian-friendly streetscapes, and integrating public transportation, cities can reduce the reliance on cars and minimize conflicts between pedestrians and vehicles. This can lead to a safer environment for all road users.
8. How can technology help improve pedestrian safety?Advancements in technology can contribute to pedestrian safety in various ways. Examples include vehicle safety features such as pedestrian detection systems, automatic emergency braking, and improved street lighting. Additionally, the development of smartphone applications and other tools can provide real-time information on traffic conditions and safe routes for pedestrians.
9. Are there specific age groups most people that are more at higher risk now for pedestrian accidents?Children and older adults are often more vulnerable to driver and pedestrian accidents due to factors such as limited mobility, slower reaction times, and lower visibility. Ensuring safe routes to schools and providing age-friendly infrastructure in parking lots can help protect these vulnerable populations from dangerous car collisions.
10. How can community involvement play a role in improving pedestrian safety?Community involvement in intersection and can be crucial in identifying areas of intersection and concern and advocating for improvements.
Remember, creating a safer environment for pedestrians is a shared responsibility.
11. How do speed limits vary between different road types?
Speed limits are usually determined based on the type of road, surrounding environment, and the presence of pedestrians or cyclists. In residential areas and school zones, lower speed limits are enforced to protect vulnerable road users. On highways and freeways, higher speed limits are permitted due to the absence of pedestrian traffic and a lower risk of collisions.

